What is the ECS?
Key Points
- One of the management systems of the body
- Activated by Endocannabinoids such as Anandamide and 2AG
- Activated by Phytocannabinoids found in Cannabis
- The ECS is involved in a wide variety of process including pain, memory, mood, appetite, stress, sleep, metabolism, immune function, and reproductive function.
- Medical Cannabis is used to target the EC system to bring the body into balance.
The Endocannabinoid System was discovered by researchers looking at how Cannabis worked.
The Endogenous Cannabinoid System, named after the plant that led to its discovery, is perhaps the most important physiologic system involved in establishing and maintaining human health.
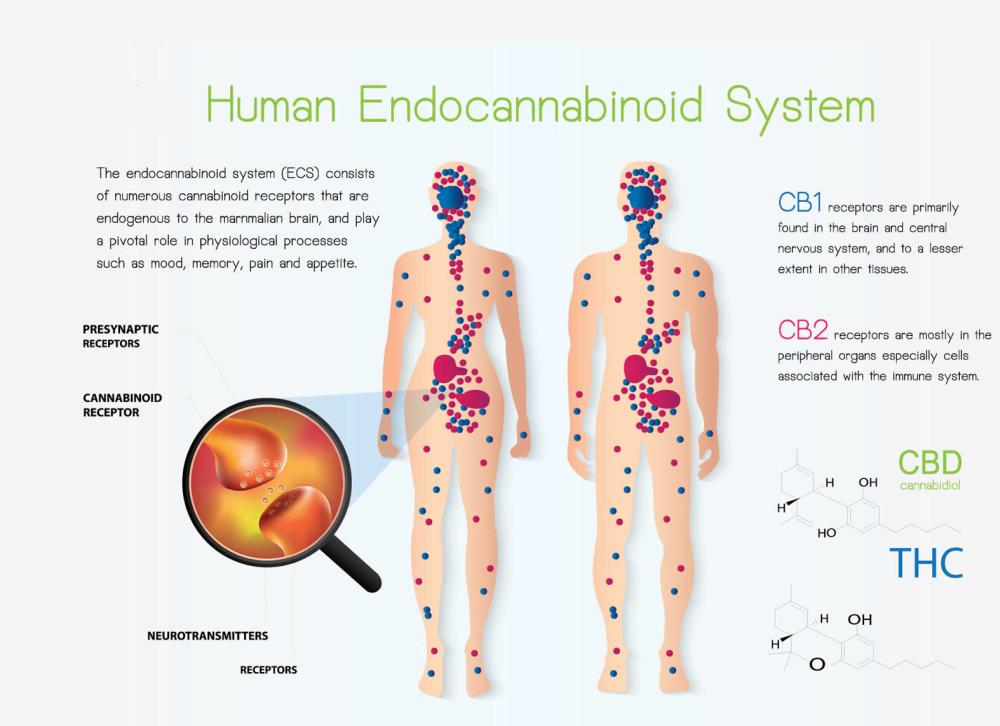
The ECS is a currently described by receptors CB1, CB2 and several other receptor candidates that interact with signalling Cannabinoids that are produced responses in the network. This network of receptor throughout the body operate in conjunction with Cannabinoids as a control system to balance the body processes with the aim of creating homeostasis in the body.
The very nature of the EC system is to manage processes in the body coordinating many sub systems, this is why the ECS can impact many different areas of the body and conditions associate with it. The endocannabinoid system has complex interactions with the immune and nervous systems. It is also present in all of the body’s organs, it is the Synergy between body and mind, this is why it is so powerful. Understanding the EC system, we begin to see a holistic approach to medicine.
The ECS is around 600 million years old being seen in some of the earliest surviving life forms such as nematodes. ECS receptors are found throughout the body in Cell membranes.
CB1 receptors are found primarily in organs including the brain.
CB2 receptors are found mainly in the immune system.
There are many more receptors that are being looked at as part of the ECS network, research is ongoing.
EndoCannabinoids produced by the body are the signals that interact with these receptors. The two most widely understood are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). These Cannabinoids are produced from cell membranes and have a local effect and short half-life. They are then degraded by the enzymes fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL).
PhytoCannabinoids are Cannabinoids produced by plants and can activate the EC system in a variety of ways. We do need more research but what is clear is a functioning and tuned Endocannabinoid system is essential for a healthy life.
The New NICE guidelines on pain management highlight pharma is not the answer and are now advocating Cognitive behaviour therapy, exercise and Anti-depressants.
Traditional medical systems of the past in India, China, Tibet and Thailand understood cannabis could provide this function and are now restoring the historic preparations.
The presence of the ECS and the way Phyto cannabinoids (Phyto meaning of plant origin) like THC and CBD interact with the cannabinoid receptors suggest strong potential for the efficacy of cannabis as a medicine. Also, the diverse range of bodily functions governed by the ECS, indicates the potential disorders and illnesses that may be treated by cannabinoid medicines.
Along with this, ongoing research continues to support the efficacy of medical cannabis and points to the potential for cannabis to become an effective medicine
We need to go back to the future to develop better lifestyles and use natures treasure chest to live more holistically to stay well.
Western Medicine is finally and slowly coming to realise this. Please make sure your Doctor understands the Endocannabinoid system.
ECS Receptors
- CB1 Receptors are concentrated in the brain & the central nervous system but are also present in some organs.
- CB2 Receptors are mostly in peripheral organs, especially cells associated with the immune system.
- GRP18 Receptors are found primarily in bone marrow, the spleen and lymph nodes and to a lesser extent the testes.
- GPR55 Receptors are found in the bones, the brain, particularly the cerebellum, and the jejunum and ileum.
- GPR119 Receptors are found concentrated in the pancreas and the intestinal tract.
- TRPV1 Receptors are concentrated in the blood, bone, marrow, tongue, Kidney, liver, stomach and ovaries.
- TRPV2 Receptors are concentrated in the skin, muscle, kidney, stomach and lungs.
- TRPV3 Receptors are expressed in subsets of the human sensory neurons that terminate in the skin and are activated at distinct physiological temperatures.